 2025.07.22
2025.07.22
 Industry News
Industry News
A brake booster is a critical component in modern vehicle braking systems that amplifies the force applied to the brake pedal, making it easier to stop the vehicle. This guide will explain everything you need to know about brake boosters, including their function, types, common problems, and maintenance tips.
The brake booster uses vacuum pressure or hydraulic pressure to multiply the force your foot applies to the brake pedal. Here's the basic operation:
| Type | How It Works | Common Applications |
| Vacuum Brake Booster | Uses engine vacuum to amplify pedal force | Most gasoline-powered vehicles |
| Hydraulic Brake Booster | Uses power steering pump pressure | Some diesel vehicles and performance cars |
| Electric Brake Booster | Uses an electric motor to provide boost | Hybrid and electric vehicles |
Understanding the main components will help you diagnose problems:
Watch for these symptoms of a failing brake booster:
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
| Hard brake pedal | Vacuum leak, failed diaphragm |
| Hissing noise when braking | Vacuum leak in booster or hose |
| Engine stalls when braking | Severe vacuum leak |
| Brake pedal doesn't return properly | Internal booster problem |
| Reduced braking power | Partial booster failure |
You can perform these simple tests to check your brake booster:
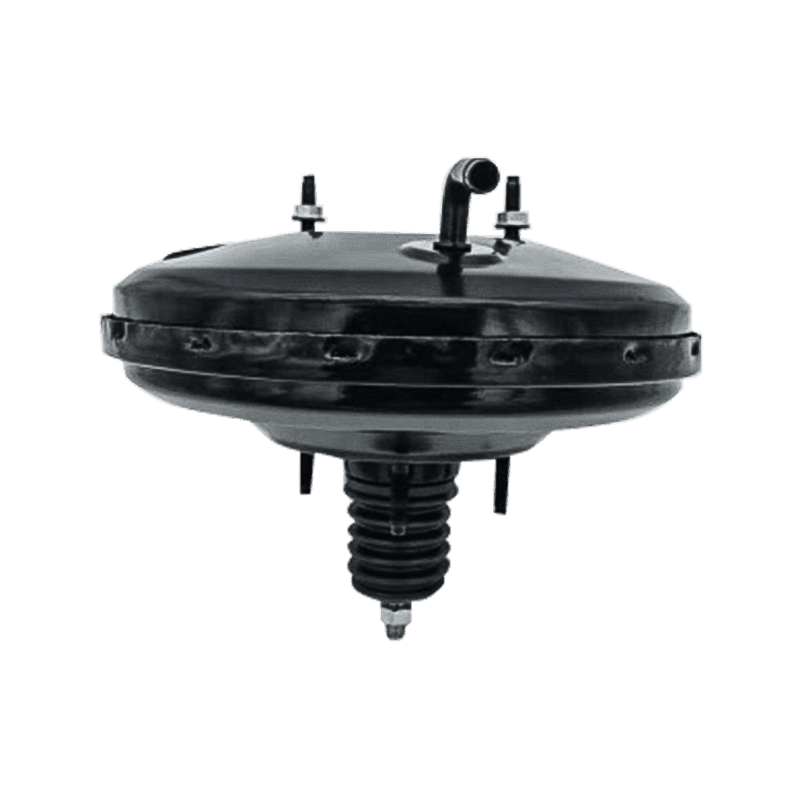

Replacement costs vary depending on vehicle type:
| Component | Average Cost Range |
| Brake booster unit | $100-$400 |
| Labor costs | $150-$300 |
| Total replacement cost | $250-$700 |
Proper maintenance can extend your brake booster's life:
Many people confuse these two components:
| Feature | Brake Booster | Master Cylinder |
| Function | Amplifies pedal force | Converts force to hydraulic pressure |
| Location | Between pedal and master cylinder | Between booster and brake lines |
| Failure symptoms | Hard pedal, hissing noise | Soft pedal, fluid leaks |
While possible, it's dangerous. The brakes will require much more pedal force to stop the vehicle, increasing stopping distances.
Most last 100,000-150,000 miles, but proper maintenance can extend their lifespan.
Some components like check valves and vacuum hoses can be replaced, but internal failures usually require complete booster replacement.
Yes, they use electric brake boosters that don't rely on engine vacuum.
The brake booster is an essential safety component that makes modern braking systems effective and easy to use. Understanding how it works, recognizing failure symptoms, and performing proper maintenance will help ensure your vehicle's braking system remains reliable. If you suspect brake booster problems, have it inspected by a qualified technician immediately, as braking system issues can compromise vehicle safety.